

It went along with increased surgical success rates, heightened confidence of surgical practitioners and a considerable expansion of the surgical domain. Following its propagation by the British surgeon Joseph Lister in the 1860s, the use of antisepsis to prevent wound disease by killing living germs precipitated unprecedented changes in surgery. The alignment led to ‘asepsis’ as a new strategy of combating wound disease, replacing or supplementing the older practice of ‘antisepsis’. This paper discusses how surgeons eventually followed Pasteur’s advice and aligned their field of activity to laboratory science in specific ways, as, vice versa, laboratory work on bacteriology was shaped by surgical concerns in a process of mutual realignment. The power of controlling microorganisms in the laboratory was to be transferred to a specific part of the outside world – the operating room. In the passage above, he recommends adopting the same strategy in the surgical work environment. These were the kinds of technologies that had enabled Pasteur to subject microorganisms to control by his eyes and hands and allowed him to make far-reaching claims about the cause of infectious diseases and ways to prevent them. Furthermore, he ‘would use only lint, bandages and sponges previously exposed to air temperatures of 130– and use water that had been heated to temperatures of 110– ’.
Pasteur did this in his laboratory with all objects that came into contact with his microbial cultures, in order to avoid contamination. “Handwashing” by Linda Hartley (CC BY 2.If he were a surgeon, the laboratory scientists Louis Pasteur wrote in 1878, he would not only clean his instruments thoroughly, ‘but after having cleaned my hands with the greatest of care, I would subject them to rapid flaming’. Following the standard procedures in any kind of a surgical or medical intervention is extremely important because it prevents the transmission of pathogens from the environment into the patient’s body.ġ. The difference between surgical and medical asepsis depends on the extent to which disease-causing agents are controlled. Sterile techniques are followed in changing dressings of a wound, catheterization, and surgeries.Īs clear from this article, both surgical and medical asepsis minimize the risk of infections.

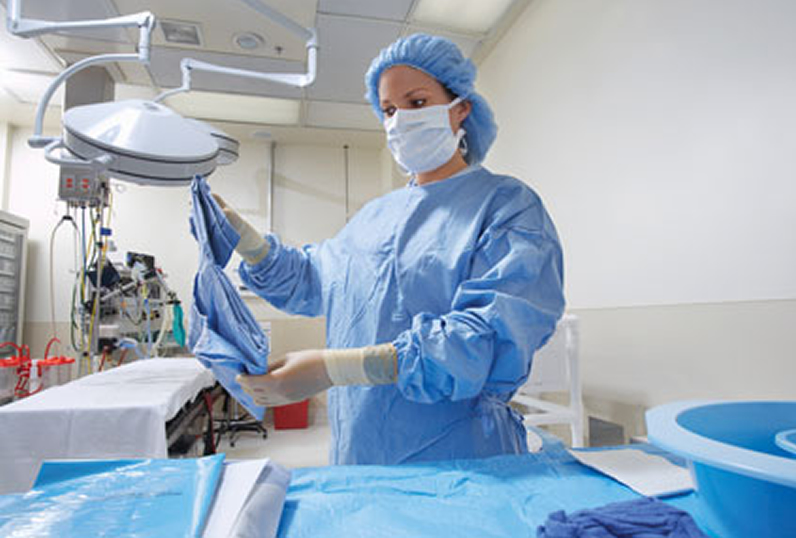
This procedure is carried out in the administration of enemas, medications, tube feedings, etc. In surgical asepsis, sterile techniques are used. The techniques used in the process are called clean techniques. Surgical asepsis is the complete elimination of the disease-causing agents and their spores from the surface of an object. Medical asepsis is the reduction of the number of disease-causing agents and their spread. Wash the hands in running water with soap.
#Medical and surgical asepsis. skin#
If you are a healthcare professional it is good to keep your nails short and always make sure that breaches of the skin are properly covered. Hand washing is an important aspect of the medical asepsis. Side by Side Comparison – Medical vs Surgical Asepsis in Tabular Form Similarities Between Medical and Surgical Asepsisĥ. On the other hand, the complete elimination of the disease-causing agents and their spores from the surface of an object is called the surgical asepsis.

The key difference between medical asepsis and surgical asepsis lies in the way they are defined. Asepsis can be broadly divided into two main categories known as medical asepsis and surgical asepsis.
#Medical and surgical asepsis. free#
The state of being free from disease-causing agents is defined as the asepsis. Key Difference – Medical vs Surgical Asepsis


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
